One of the big headlines over the weekend is LockBit, the high-profile Russian ransomware gang, decided to expand its portfolio of potential victims by creating and releasing its first macOS payload, potentially triggering members of the Apple community to panic. But have no fear: Apple security experts have dissected the payload, taking a deep dive into what it can and cannot do, and concluded that the ransomware is, actually, toothless.
“Yes, it can indeed run on Apple Silicon. That is basically the extent of its impact,” says Patrick Wardle (@patrickwardle), known macOS cybersecurity expert and founder of the non-profit, Objective-See. “macOS users have nothing to worry about.”
Here’s why.
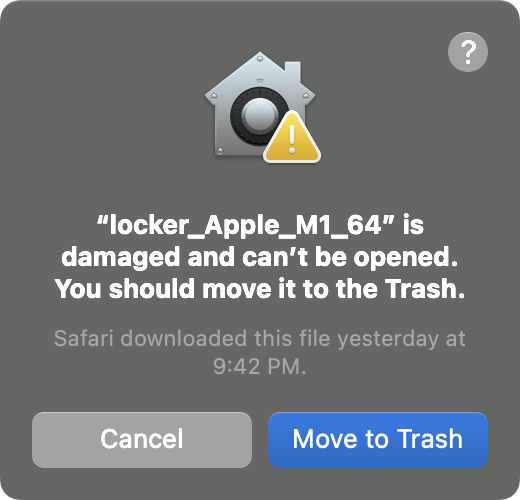
The signature is invalid.
Using a utility called codesign, Wardle saw that the payload’s signature value is “ad-hoc” compared to an Apple Developer ID. Because the signature is invalid, macOS won’t execute it.
The payload is likely a test file.
Azim Khodjibaev (@AShukuhi), a security researcher at Cisco Talos, floated the theory to BleepingComputer that the payload and its other variants designed for other OSs were “meant as a test and were never intended for development in liver cyberattacks.”
Wardle further confirmed this theory, stating it’s far from complete. Indicators in the payload’s code suggest it’s Linux-based but compiled for macOS with basic configuration settings included. The code also shows its developers have yet to consider macOS’s TCC (Transparency, Consent, and Control) and SIP (System Integrity Protection), two security features meant to protect user files and folders.
With TCC and SIP present, this payload will only be able to encrypt a little, if at all.
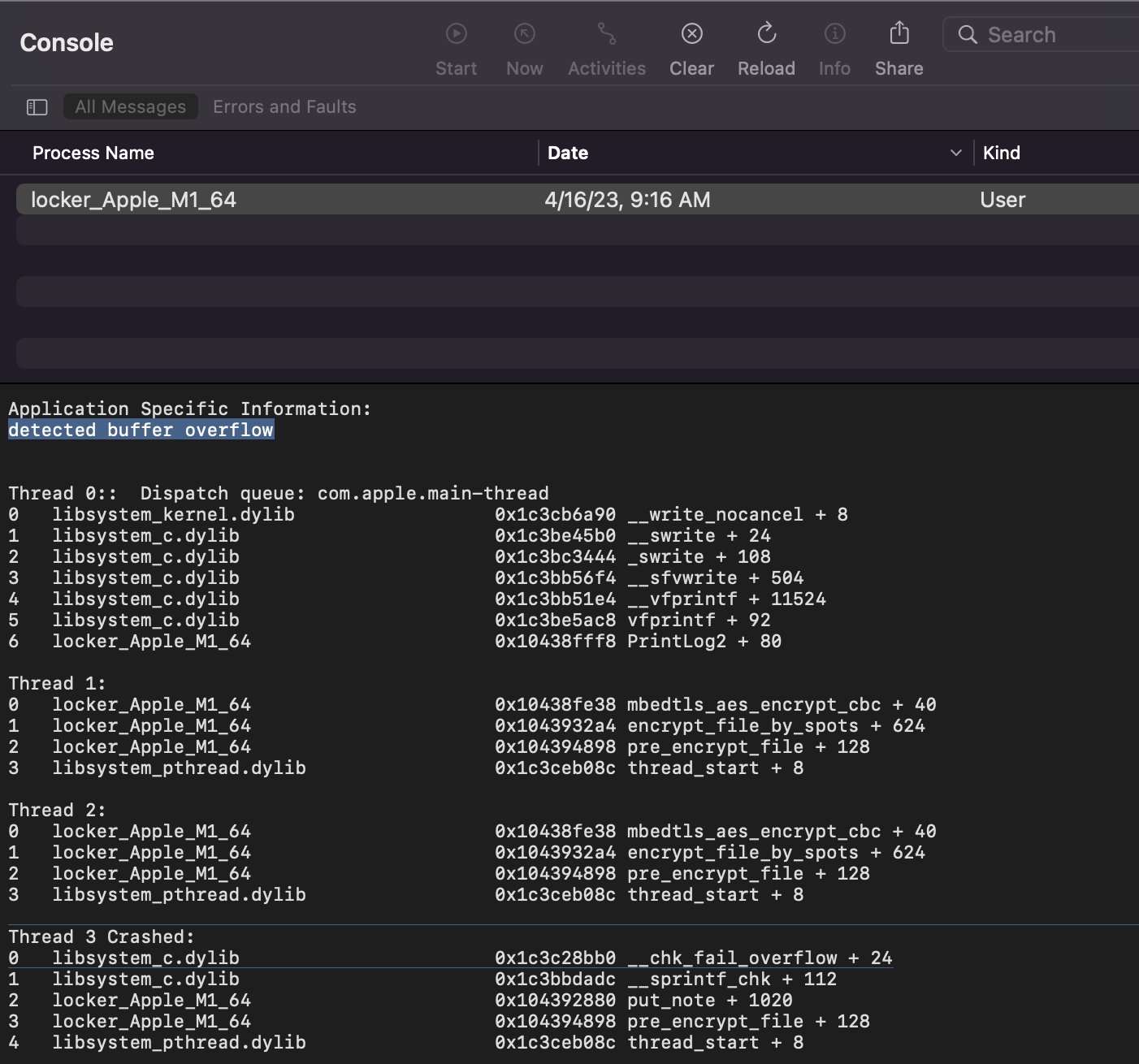
The code is buggy.
Laying further credence to test file theory, Wardle finds the macOS payload contains a buffer overflow, which will cause it to crash when executed.
Malwarebytes doesn’t detect this ransomware sample for two reasons: (1) we generally don’t detect non-functional malware test files, and (2) we only detect actual malware on Mac and not individual files.
No worries for now!
Apple users can rest easy knowing that this macOS ransomware, as it is now, will hardly impact anyone. However, as Wardle quickly pointed out, this may be different in future releases.
“The fact that a large ransomware gang has apparently set its sights on macOS should give us pause for concern and also catalyze conversations about detecting and preventing this (and future) samples in the first place,” he says in his blog.
With LockBit operating as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) outfit, its ambition is to offer a range of ransomware. Currently, we have at least two available offerings: LockBit Black (based on BlackMatter’s code) and LockBit Green (based on Conti’s code). So expanding to target systems outside its repertoire is not only a logical move but also strategic.
“For most organizations, the main takeaway is Macs are probably safe, for now, but your Windows servers were always the prime target anyway,” says Malwarebytes Security Evangelist Mark Stockley. “I’d be very surprised if there were very many Mac-only organizations of any size.
In an interview with BleepingComputer, LockBit’s public-facing representative LockBitSupp says the Mac encryptor is “actively being developed.”
How to avoid ransomware
- Block common forms of entry. Create a plan for patching vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems quickly; disable or harden remote access like RDP and VPNs; use endpoint security software that can detect exploits and malware used to deliver ransomware.
- Detect intrusions. Make it harder for intruders to operate inside your organization by segmenting networks and assigning access rights prudently. Use EDR or MDR to detect unusual activity before an attack occurs.
- Stop malicious encryption. Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response software like Malwarebytes EDR that uses multiple different detection techniques to identify ransomware, and ransomware rollback to restore damaged system files.
- Create offsite, offline backups. Keep backups offsite and offline, beyond the reach of attackers. Test them regularly to make sure you can restore essential business functions swiftly.
- Don’t get attacked twice. Once you’ve isolated the outbreak and stopped the first attack, you must remove every trace of the attackers, their malware, their tools, and their methods of entry, to avoid being attacked again.
Malwarebytes removes all remnants of ransomware and prevents you from getting reinfected. Want to learn more about how we can help protect your business? Get a free trial below.